June 20, 2025 · Jimeng Sun, PhD, CEO of Keiji AI
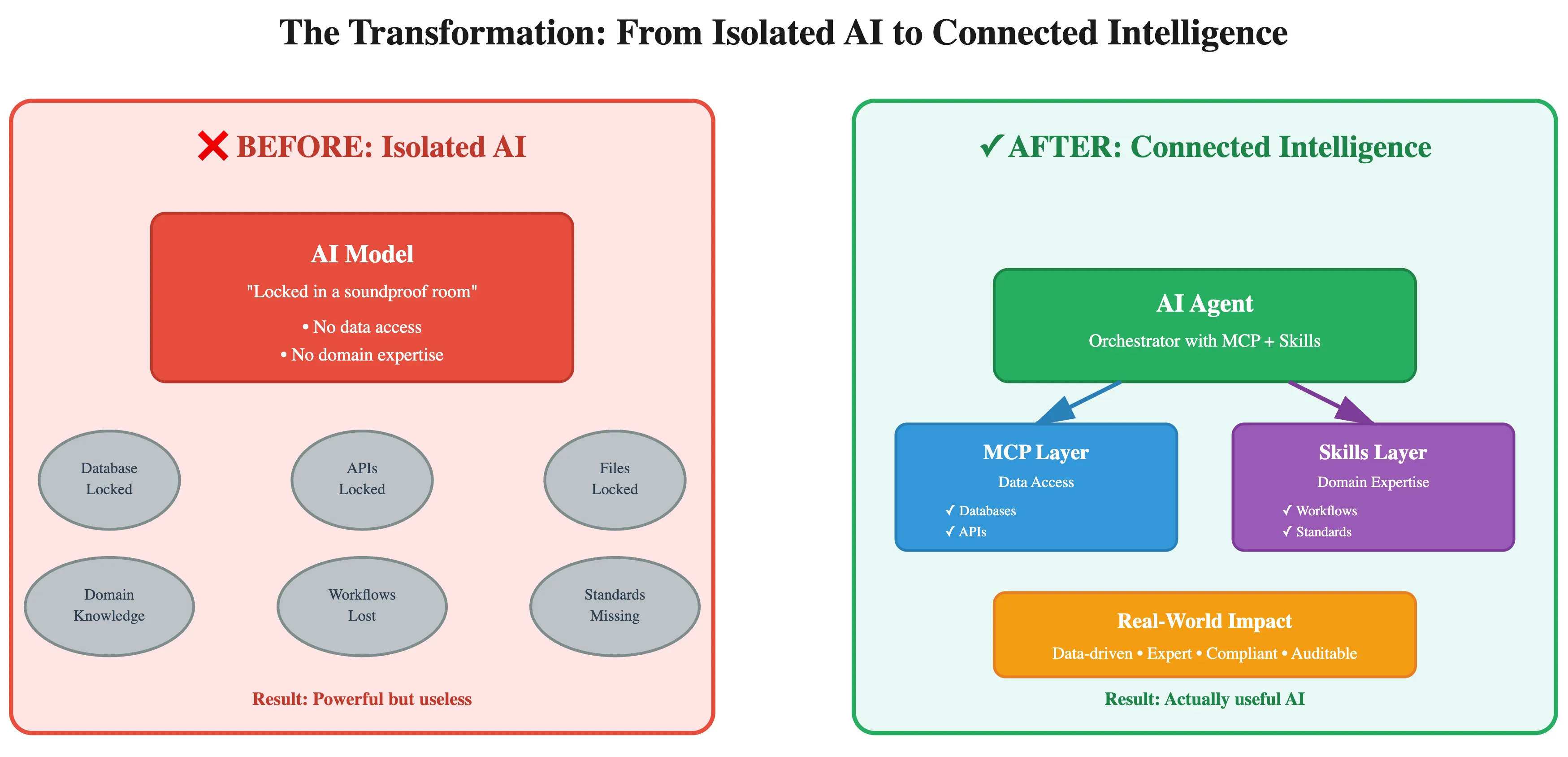
With pharmaceutical companies spending over $50 billion annually on clinical development while facing 90% failure rates, the strategic imperative for AI-driven innovation has never been clearer. This transformation hinges on overcoming fundamental challenges: the isolation of Large Language Models (LLMs) from real-world data, the fragmentation of data sources, and the stringent regulatory demands of the biomedical sector.
Enter the Model Context Protocol (MCP), an open standard introduced by Anthropic in late 2024, aiming to be the "USB-C port for AI applications". MCP standardizes how AI models securely interact with external data sources and tools, replacing bespoke, one-off integrations with a unified, scalable protocol. This architectural shift is not merely an API evolution but a paradigm shift in integration philosophy, enabling truly context-aware and actionable AI systems.
For a system like Keiji AI's TrialMind, an advanced suite of AI agents dedicated to supporting clinical research, performing data analysis and optimizing clinical trials, MCP is not just beneficial — it's foundational. By leveraging MCP, TrialMind agents can overcome the limitations of isolated LLMs, delivering precise, auditable, and real-time insights across the entire drug development lifecycle.
The Technical Foundation: MCP's Architecture for Agentic AI
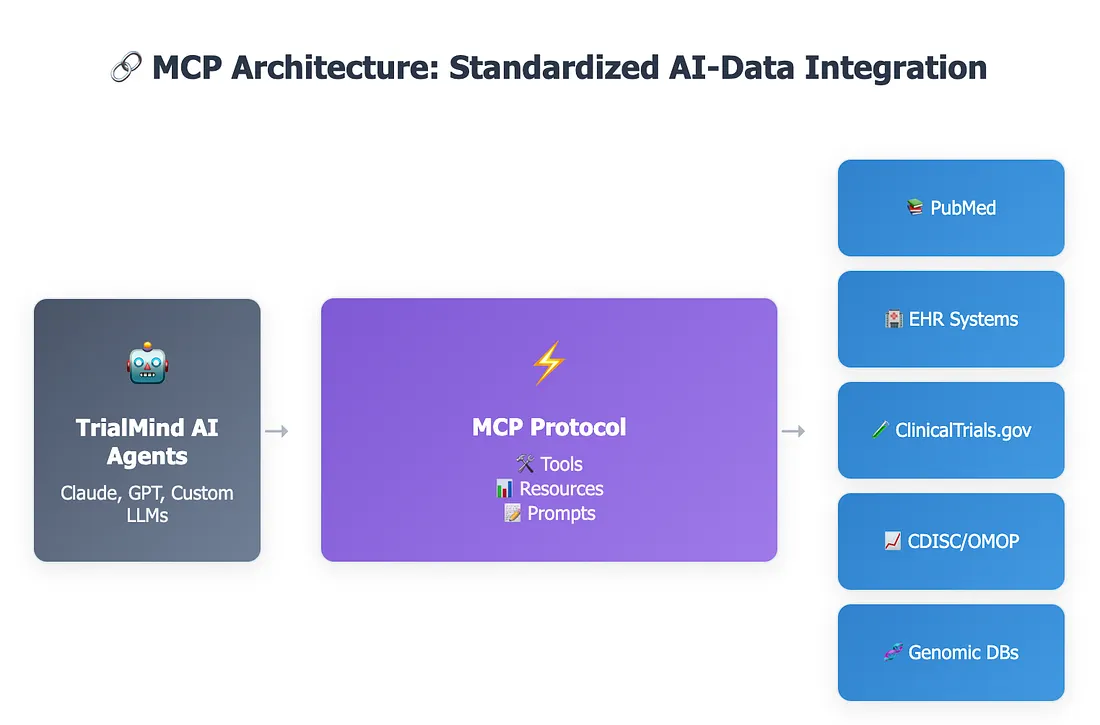
MCP operates on a client-server architecture. MCP Servers are lightweight programs that expose specific data sources or functionalities via the MCP standard, while MCP Clients (embedded within AI applications like Claude Desktop or other AI tools) connect to these servers, relaying requests and responses between the AI model and external systems. Communication between clients and servers is typically JSON-based (using JSON-RPC), making it language-agnostic.
The protocol defines core "primitives" that an AI can interact with on the server side:
- Tools: Executable functions that allow the AI to perform actions in the external world, such as querying a database, searching the web, or manipulating files.
- Resources: Structured data or documents that the server can send to the AI, enriching its context.
- Prompts: Pre-defined instructions or templates that can guide AI interactions or formatting.
This structured approach allows AI agents to dynamically discover and utilize capabilities without rigid, predefined calls, transforming traditional APIs into context-aware capabilities.
TrialMind Agents in Action: Leveraging MCP for Clinical Trial Optimization
Let's explore how MCP enables specific TrialMind agent functionalities in the complex clinical trial environment:
1. TrialMind-SLR: Literature Mining Agent for Systematic Literature Reviews
For pharmaceutical R&D and biotech research, scientists require seamless access to a multitude of information sources: scientific literature, patents, genomic datasets, and internal experimental results. A vanilla LLM is limited to its training data cutoff date, rendering it "blind" to current information.
TrialMind-SLR, powered by MCP, overcomes this by integrating with specialized biomedical data sources through standardized server implementations. MCP's flexible architecture enables seamless connectivity to authoritative research databases, providing "tools" that can:
- Query PubMed: An MCP-enabled LLM, part of TrialMind-Lit, can invoke a literature_search tool to dynamically retrieve the latest scientific papers based on specific keywords (e.g., "inhibitors of protein XYZ reported in the last 5 years"). This ensures the AI's insights are always grounded in current research, moving beyond its static training data.
- Search ClinicalTrials.gov: The agent can utilize a trial_searcher tool to find ongoing or completed clinical trials for specific conditions or with certain genetic markers. This streamlines competitive landscape analysis and trial design.

Technical Insight: The elegance lies in MCP standardizing the invocation. Instead of bespoke API calls for each database, TrialMind-Lit's LLM sends a structured MCP request to specialized data servers. These servers then handle the complexities of querying PubMed's API or ClinicalTrials.gov's underlying database, abstracting this detail from the AI model and presenting the results in a format the LLM can readily consume as context. This dramatically enhances productivity by eliminating manual website visits or complex query writing.
2. TrialMind-DSA: Data Science Assistant
Pharma organizations face persistent challenges due to fragmented clinical and real-world data across EHRs, registries, CDISC/OMOP repositories, and legacy data systems. TrialMind-Data, powered by Keiji AI's foundation model and MCP (modular connector protocol), acts as an enterprise-grade data science assistant, enabling seamless access, analysis, and auditability across these diverse datasets.
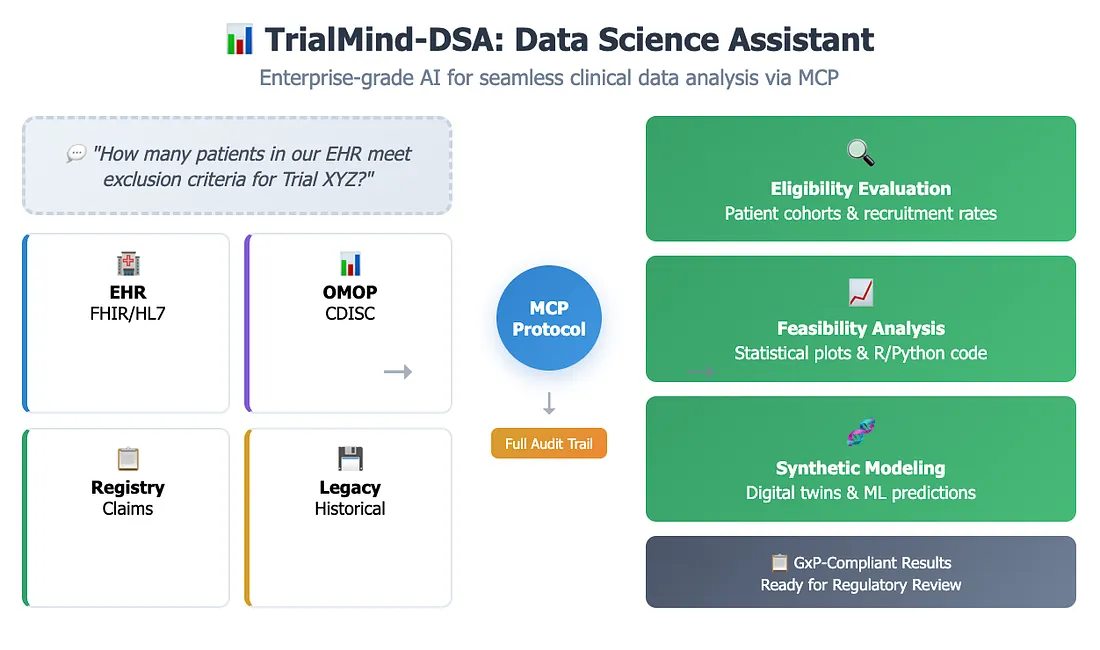
Eligibility Criteria Evaluation
TrialMind-Data can dynamically evaluate protocol criteria against real-world EHR or claims datasets by querying CDISC/OMOP-compliant databases. For example, a user might ask, "How many patients in our EHR meet the exclusion criteria for Trial XYZ?" TrialMind-Data can retrieve the matched cohort, estimate recruitment rates, and generate visualizations — all without writing code.
Real-Time Feasibility Analysis
Instead of relying on static Excel templates, teams can use TrialMind-Data to ask in natural language: "What are the time-to-treatment distributions for 2L NSCLC patients in our dataset?" The agent interfaces with structured databases and statistical libraries to return plots, summary statistics, and reusable R or Python code for further validation.
Synthetic Data Validation and Modeling
With access to synthetic patient data generated by TrialMind's digital twin module, TrialMind-Data can simulate rare population cohorts, run stratified analyses, or test ML-based outcome prediction models. This is especially useful for exploring protocol modifications or augmenting small datasets during study planning phases.
Technical Insight: Every interaction through TrialMind-Data is logged through the MCP architecture — recording access history, parameter settings, and analytical output — enabling full audit trails required for GxP compliance. For example, if a regulatory reviewer questions the basis for eligibility rates used in trial design, the system can trace back to the original query, source dataset, and code used, ensuring transparency and reproducibility.
3. TrialMind-Optimize: AI Agents for Trial Design, Recruitment, and Outcome Prediction
Modern clinical development is overwhelmed by data complexity and cross-functional dependencies. TrialMind-Optimize, powered by Keiji AI's suite of specialized AI models and the MCP (Modular Connector Protocol), provides intelligent agents that support protocol optimization, patient recruitment, and trial outcome forecasting — enabling smarter, faster clinical trials.
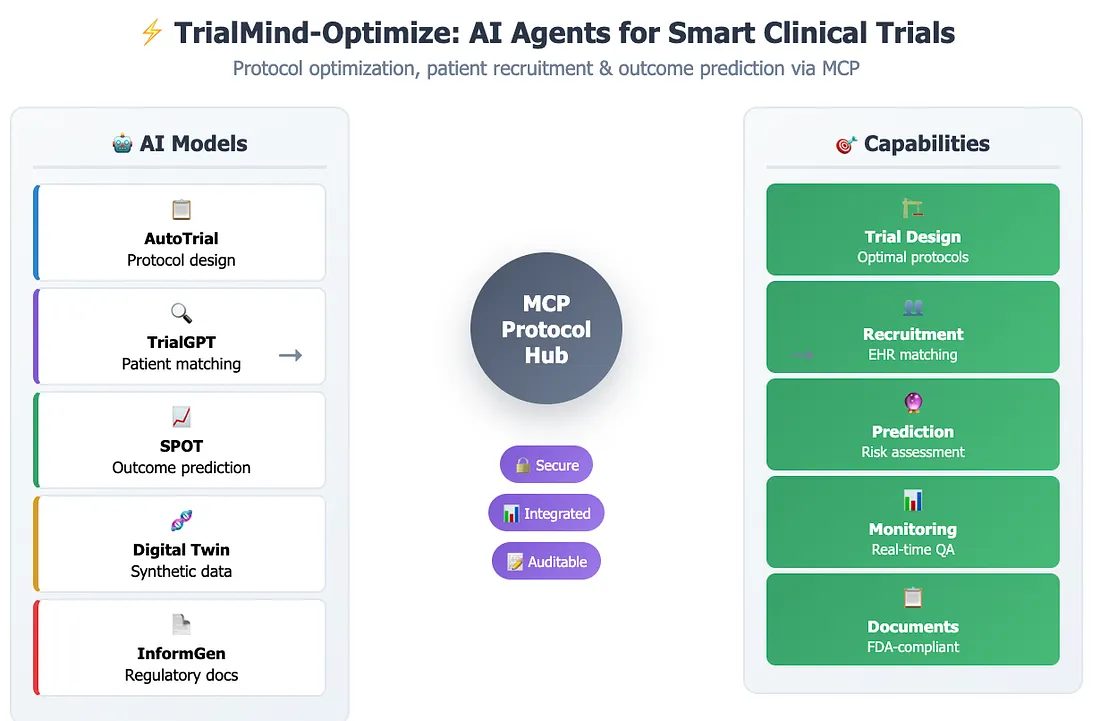
Trial Design & Eligibility Optimization
TrialMind-Optimize includes AutoTrial, a specialized model that generates inclusion/exclusion criteria aligned with target indication, endpoint, and protocol objectives. By analyzing 400K+ historical clinical trials and incorporating user prompts, the model produces customized eligibility drafts that improve both regulatory alignment and recruitment feasibility. Through MCP, it can retrieve protocol precedents from internal repositories for comparative analysis.
Patient Recruitment & Trial Matching
Leveraging TrialGPT, TrialMind-Optimize uses natural language to identify suitable patients from EHR systems integrated via FHIR-based MCP servers. The model ranks and explains trial matches better than clinicians, achieving >90% recall and 87% explanation accuracy. When integrated with site data, it automatically filters patients based on trial criteria and prioritizes those most likely to enroll.
Trial Outcome Prediction & Simulation
TrialMind's SPOT model (Sequential Predictive Modeling of Trial Outcomes) forecasts trial results based on baseline characteristics, previous trial data, and simulated patient cohorts. This capability allows teams to assess risk, refine endpoints, or redesign arms — especially useful in oncology or rare disease trials. Combined with synthetic patient data generated by TrialMind's Digital Twin module, users can simulate counterfactuals to test design decisions before costly execution.
Ongoing Monitoring & Quality Assurance (QA)
TrialMind-Optimize connects to EDC systems via MCP to track trial progress in real-time. It flags anomalies such as protocol deviations, overdue labs, or serious adverse events. Because every interaction is logged with precise version control, TrialMind ensures full GxP-compliant audit trails — supporting regulatory inspections and internal QA.
Regulatory Document Assembly
When generating submission-ready content — such as efficacy summaries, informed consent forms, or SAP appendices — TrialMind-Optimize pulls from validated sources using versioned MCP calls. Models like InformGen assist in drafting site-customized, regulation-compliant documents with alignment to FDA guidelines.
Technical Insight: MCP's modularity and traceability enable scalable, enterprise-ready deployment of AI agents. Each connector acts as a secure, auditable interface to internal systems — whether clinical data warehouses, document repositories, or trial protocol archives. TrialMind's models can reuse these interfaces across functions, speeding up AI integration and reducing compliance burden. For proprietary systems, Claude 4, or similar LLMs can even co-develop new MCP servers, accelerating integration cycles.
The Future of Clinical Trials: A Unified AI Ecosystem
MCP, and its application in agent suites like Keiji AI's TrialMind, signifies a profound shift in how AI systems will integrate into clinical trials. By providing a common "language" and framework for AI-data interactions, MCP allows for:
- Enhanced Interoperability: AI models can dynamically integrate with diverse systems (EHRs, LIMS, databases, web services) from various vendors, fostering a rich, connected ecosystem.
- Robust Security & Compliance: MCP's built-in features for secure connections, granular permissions, standardized authentication, and comprehensive logging transform AI from a "black box" into a transparent, governable system. This is paramount for meeting FDA/EMA expectations for AI transparency, reproducibility, and data privacy.
- Reproducibility and Auditability: The ability to capture the entire context of an AI operation — including tool calls, data retrieved, and versions — is a game-changer for scientific rigor and regulatory accountability.
- Reduction of Hallucinations: By enabling real-time queries to authoritative sources, MCP grounds AI responses in factual data, significantly reducing the likelihood of generating incorrect or outdated information.
- Scalability for Agentic AI: MCP facilitates complex, multi-step agent workflows where different AI agents or tools can collaborate, orchestrating sequences of actions across disparate systems.
With TrialMind, a clinical scientist can simply ask, "What's the expected enrollment rate for this protocol in the U.S.?" and receive a fully sourced, reproducible answer — grounded in real-world data, past trial designs, and predictive models. A biostatistician can validate interim results by querying SDTM/ADaM datasets and comparing them against SAP-defined endpoints — without writing a single line of code. A clinical data scientist can simulate alternative eligibility criteria, assess recruitment impact, and re-run time-to-event models — all with full traceability, code reuse, and statistical rigor.
Every action is explainable, every dataset is permissioned, and every result is regulatory-ready. This is not just the future of AI in clinical trials — it's what TrialMind delivers today. TrialMind is your AI-native teammate for faster, smarter, and safer clinical development.